Image Post-processing wizard page defines raster image tile processing, before stitching them together into the final image:
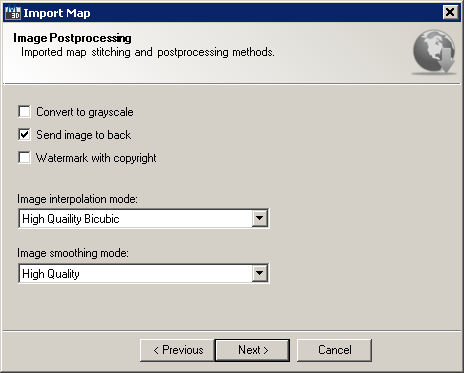
Import Map wizard Image Post-processing page
This wizard page provides following options:
It also provides following navigation buttons:
Sometimes it's necessary to simply ignore color information and represent resulting image in grayscale. Colors in an image get converted to a shade of gray by calculating the effective brightness or luminance of the color and using this value to create a shade of gray that matches the desired brightness. Checking this option results in following raster imagery:
|
|
Color image with polygon overlay |
Grayscale image with polygon overlay |
This option affects drawing order of the raster image inserted into AutoCAD. Sending image to back means positioning it below all other entities in the drawing. This equals to selecting specified image and first issuing DRAWORDER command in AutoCAD, then picking BACK option:
|
|
Send to back turned on |
Send to back turned off |
Image interpolation occurs in all imported raster imagery at some stage - whether this be in raster tile stitching or in raster scaling. It happens while TopoPlanner resizes (scales) or remaps (distorts) imported image from one pixel grid to another. Image resizing is necessary when you need to increase or decrease the total number of pixels, whereas remapping can occur under a wider variety of scenarios. There's following image interpolation modes (algorithms) available:
Even if the same image resize or remap is performed, the results can vary significantly depending on the interpolation algorithm. It is only an approximation, therefore an image will always lose some quality each time interpolation is performed. Image interpolation works in two directions, and tries to achieve a best approximation of a pixel's color and intensity based on the values at surrounding pixels. The following example illustrates how resizing / enlargement works:
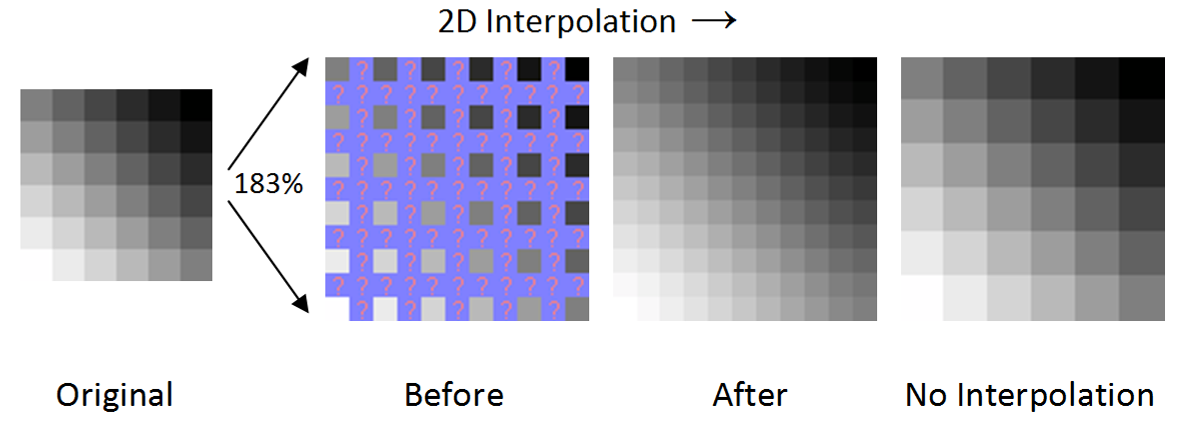
Raster image resizing with and without 2D interpolation
Most popular interpolation algorithms are explained below, on the square [0,3] X [0,3] consisting of 9 unit squares patched together. Color indicates function value. The black dots are the locations of the prescribed data being interpolated:
|
|
|
Nearest neighbor interpolation |
Bilinear interpolation |
Bicubic interpolation |
During image interpolation post-processing phase each tile may also get smoothed using specified algorithm. There's following image smoothing modes (algorithms) available:
Anti-aliasing is a process which attempts to minimize the appearance of aliased or jagged diagonal edges. These give text or images a rough digital appearance. Anti-aliasing removes jagged edges and gives the appearance of smoother edges and higher resolution. It works by taking into account how much an ideal edge overlaps adjacent pixels. The aliased edge simply rounds up or down with no intermediate value, whereas the anti-aliased edge gives a value proportional to how much of the edge was within each pixel:
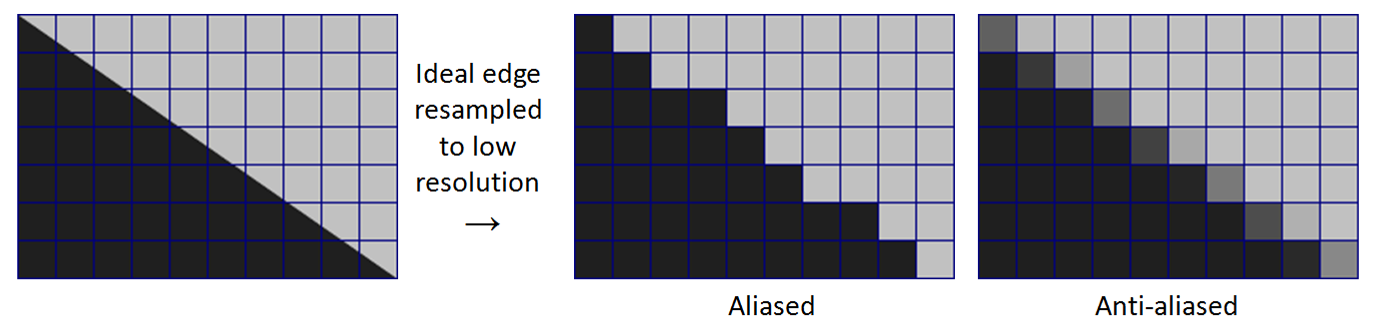
Raster image with and without anti-aliasing